Why Darker Skin Still Needs Daily Sunscreen, Here’s Why

Darker skin is often believed to have “natural protection” against the sun, leading many to think daily sunscreen isn’t necessary. While phrases like “Black don’t crack” hint that melanin-rich skin ages more slowly, dermatologists clarify that this isn’t the full story. Melanin offers some UV defense, but not enough to fully prevent sun-related damage.
Experts like Dr. Naana Boayke and Dr. Rose Ingleton explain that UV exposure can still trigger hyperpigmentation, worsen inflammation, and contribute to skin cancer—conditions that often appear subtly on deeper skin tones. Because early signs may look mild or go unnoticed, damage can progress quietly over time.
Understanding the science behind melanin and UV exposure helps break the myth that darker skin doesn’t need sunscreen. These dermatologists highlight how the misconception formed and why it’s misleading, offering practical guidance for building effective sun protection habits. With accurate knowledge, readers can make informed choices that support long-term skin health and confidence.
Do Black People Need to Wear Sunscreen?
The idea behind “Black don’t crack” is often misunderstood. As Dr. Rose Ingleton notes, melanin-rich skin may develop wrinkles more slowly, but that doesn’t mean it’s immune to UV damage. Higher melanin levels slow visible aging, yet deeper skin tones can still experience sagging, texture changes, and stubborn dark spots over time.
Dermatology research shows melanin provides a natural protection roughly equal to SPF 13, according to Dr. Naana Boakye—helpful, but far below what’s needed for long-term safety. Without additional sunscreen, UV exposure continues to cause cumulative harm that leads to hyperpigmentation and early aging.
For lighter skin, natural protection drops to around SPF 4, which is why dermatologists universally recommend wearing broad-spectrum SPF 30–50 daily.
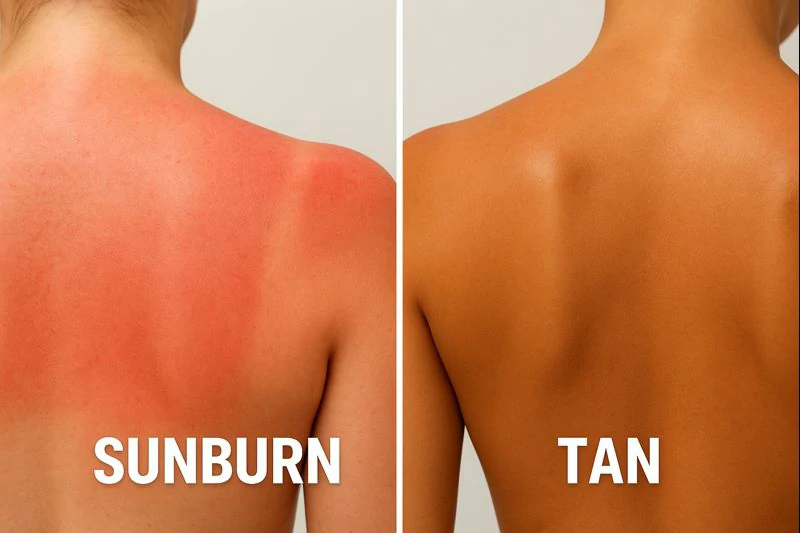
In short, darker skin may take longer to burn, but it is not resistant to UV damage. Melanin helps—but it is not a replacement for sunscreen. Consistent protection keeps the skin even-toned, healthy, and youthful.
The Potential Effects of Not Wearing Sunscreen
Skipping sunscreen can raise several skin health risks, including skin cancer. While individuals with darker skin develop skin cancer less often, Dr. Rose Ingleton explains that diagnoses frequently occur at later stages because early signs are subtle and easily missed.
UV damage on melanin-rich skin doesn’t always appear as sunburn. Instead, it may show up as small white patches, dark spots that slowly deepen, or premature laxity that doesn’t match one’s age. Repeated sun exposure without protection accelerates these issues.
Daily sunscreen is viewed by dermatologists as an essential preventative step. A suitable SPF helps block new UV damage while preventing existing hyperpigmentation from worsening. When used consistently, sunscreen supports an even complexion, smoother texture, and better long-term skin resilience.
For anyone beginning their skincare journey, understanding these gradual yet significant effects can be the key to maintaining healthy, balanced skin for years to come.
How to Pick the Right Sunscreen for Melanin-Rich Skin
Finding sunscreen that suits darker skin can be challenging, especially with older formulas that leave a white cast. Fortunately, newer chemical and mineral sunscreens are now more inclusive and blend more easily across skin tones.
Chemical sunscreens absorb UV rays and release them as heat, while mineral options like zinc oxide and titanium dioxide reflect UV from the skin’s surface. Since UVB causes burning and hyperpigmentation and UVA accelerates aging and skin cancer risk, experts strongly recommend choosing broad-spectrum protection.
Mineral sunscreens tend to leave more residue, though some improve after blending. Many melanin-rich users prefer chemical formulas because they melt into the skin without a trace.
Dermatologists agree: the best sunscreen is the one you will wear every single day, ideally SPF 30 or higher. Creams or gels help with accurate application, while sticks are convenient for reapplication and sprays work well for larger areas. Dr. Naana Boakye also suggests using SPF lip balms to protect the lips—an area often overlooked but equally vulnerable to UV damage.
Common Sunscreen Myths for Dark Skin (and Why They’re Wrong)
Many misconceptions about sunscreen and dark skin come from the belief that melanin offers full protection. Dermatologists consistently emphasize that melanin provides partial, not complete, defense against UV rays.
Common myths include:
“Dark skin can’t get sunburned.”
While sunburn appears less dramatically on deeper skin tones, dermatologists confirm it can still happen—often as warmth, irritation, or dark patches rather than the classic red burn.
“Black people don’t get skin cancer.”
Although rates are lower, skin cancer in darker skin is frequently diagnosed late because early signs are subtle. Without UV protection, the risk still rises.
“Melanin equals high SPF.”
Experts note that natural melanin protection is only comparable to a low SPF and cannot replace broad-spectrum sunscreen.
Debunking these myths empowers people with melanin-rich skin to understand what their skin truly needs. Daily broad-spectrum SPF 30 helps prevent premature aging, hyperpigmentation, and cumulative long-term UV damage—issues that often develop silently without consistent protection.
Sunscreen and Hyperpigmentation: What You Need to Know
Hyperpigmentation is one of the most common concerns among melanin-rich individuals, and sun exposure is a major, often underestimated trigger. Dermatologists explain that UVB stimulates excess melanin, intensifying dark spots, acne marks, and melasma.
Meanwhile, UVA penetrates deeper and prolongs underlying inflammation, making discoloration linger even after the original breakout or irritation has healed. This is why hyperpigmentation can be stubborn and slow to fade on darker skin.
Visible light from the sun can also worsen dark patches in some people, especially those prone to pigment changes. For this reason, medical experts recommend daily broad-spectrum SPF 30 and, when possible, formulas containing iron oxides to help protect against visible light.
Consistent sunscreen use not only reduces the appearance of existing dark spots but also prevents new ones from forming. Over time, this supports a more even, stable skin tone and smoother recovery from post-inflammatory pigmentation.
Recommended Sunscreens for Dark Skin (Dermatologist-Approved)
Dermatologists recommend sunscreens that protect effectively without leaving a white cast—a common concern for melanin-rich skin. These expert-approved options offer reliable UV defense with comfortable, daily-wear textures.
Top Picks Loved by Dark-Skin Users:
- Black Girl Sunscreen SPF 30 – No white cast, deeply moisturizing.
- Aqua+ Multi-Protection Sunscreen SPF 50+ – Lightweight, high protection for everyday use.
- Neutrogena PureScreen+ Tinted Mineral – Mineral formula with tint to blend seamlessly.
- Aegte Glass-Skin Gel SPF 50 – Ultra-fluid gel that gives a smooth, glass-skin finish.
Dermatologist Favorites:
- EltaMD UV Clear Tinted SPF 46 – Zinc oxide + niacinamide, lightweight, non-comedogenic.
- EltaMD UV Clear Deep Tinted SPF 46 – Deeper tint for richer skin tones; evens complexion.
- Supergoop! Unseen Sunscreen SPF 40 – Clear gel/primer texture, zero cast, suits all skin tones.
Why experts recommend these formulas:
- Broad-spectrum UVA + UVB protection.
- Skin-friendly textures that blend invisibly on dark skin.
- Helpful actives like niacinamide, mineral filters, and antioxidants.
- Easy for daily use and reapplication.
Choosing a dermatologist-approved sunscreen that matches your skin tone ensures effective UV protection without compromising comfort or finish.





 Acne
Acne Anti-Aging
Anti-Aging Business
Business Digital Marketing
Digital Marketing Economics
Economics Exfoliation
Exfoliation Hair Removal
Hair Removal Movies
Movies Personal Finance
Personal Finance Websites
Websites