Deodorant vs. Antiperspirant: How to Choose (Dermatologist Guide)

Many people still assume deodorant and antiperspirant are interchangeable, but from a dermatological and biochemical standpoint, they serve very different purposes. Understanding this difference is essential, especially if you are just starting a skincare or personal care routine.
According to board-certified dermatologists Dr. Hooman Khorasani, MD, FAAD, and Dr. Teresa Song, MD, FAAD, choosing between deodorant vs. antiperspirant should be based on how your body naturally produces sweat and odor—not just fragrance preference.
In simple terms, deodorants are designed to control body odor, while antiperspirants are formulated to reduce sweat production. Deodorants target odor-causing bacteria on the skin, whereas antiperspirants use active ingredients, such as aluminum salts, to temporarily block sweat ducts and minimize moisture.
This distinction matters because excessive moisture and trapped bacteria can increase irritation, discomfort, and odor. Selecting the right product helps support underarm skin health and daily confidence. Continue reading to learn how each product works and which option best fits your lifestyle and skin needs.
What Is Deodorant and How Does It Work?
Deodorant is a personal care product formulated to reduce or mask body odor rather than stop sweating. Dr. Hooman Khorasani, MD, FAAD, explains that deodorants primarily work through antimicrobial action and fragrance, making them ideal for people with normal sweat levels.
From a physiological perspective, the body has two main types of sweat glands: eccrine and apocrine glands. Odor mainly originates from apocrine glands, which release protein-rich sweat. When skin bacteria break down this sweat, odor-causing compounds are produced.
Deodorants address this process by:
- Reducing odor-causing bacteria, helping limit the breakdown of sweat
- Providing fragrance, which helps maintain a fresh scent throughout the day
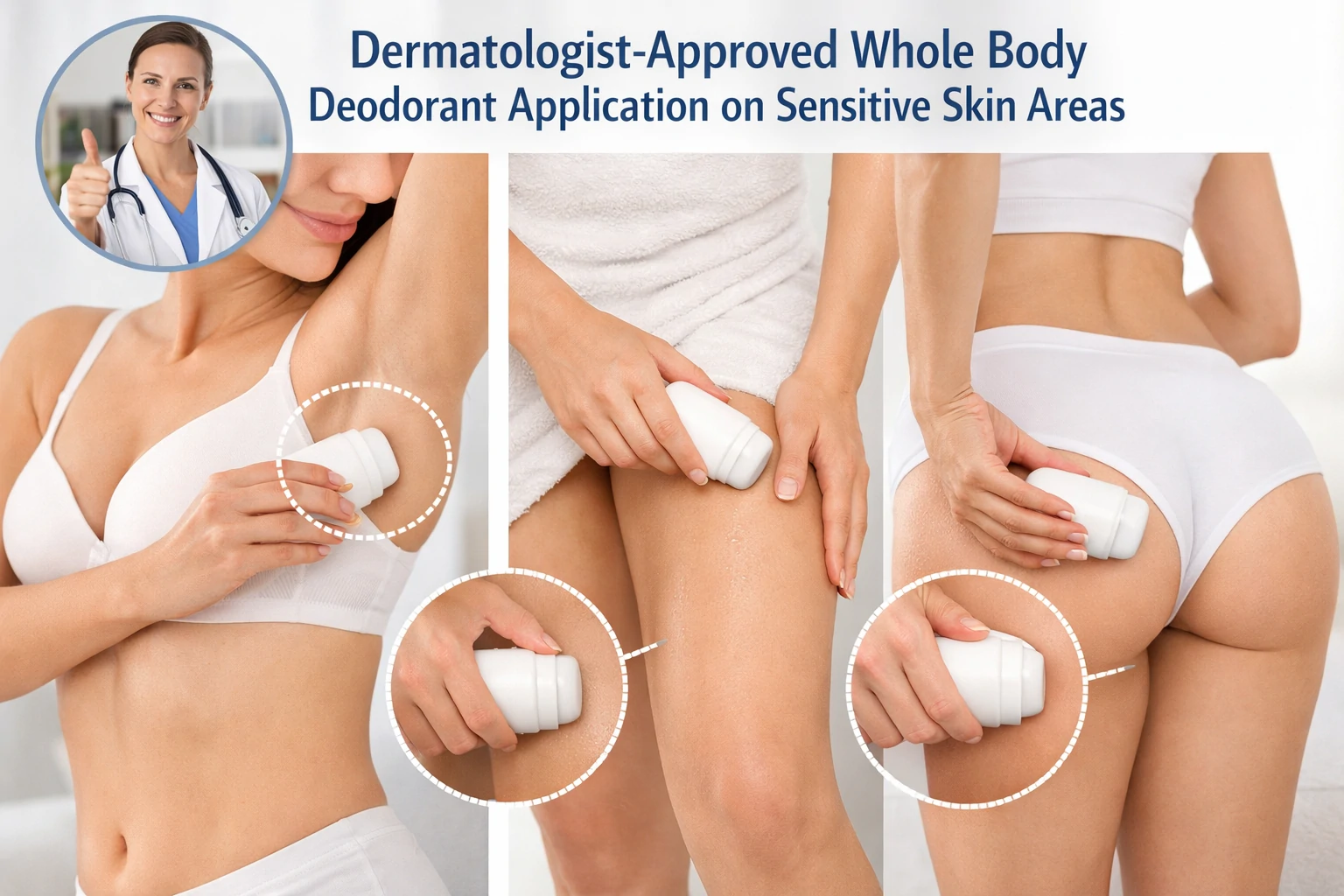
Because deodorants do not block sweat glands, they allow the skin to breathe naturally. This makes them a popular choice for individuals with sensitive skin or those seeking a lighter, everyday underarm care solution without pore blockage.
Pros and Cons of Using Deodorant
From a skincare perspective, deodorant offers high flexibility and ease of use. It is available in multiple formats—stick, spray, roll-on, and gel—allowing users to choose a texture that suits their daily routine and comfort level. Functionally, deodorant is effective at controlling body odor, which helps maintain confidence throughout the day, especially for those with normal sweat production.
However, a balanced, medical view is important. Board-certified dermatologist Dr. Hooman Khorasani, MD, FAAD, notes that some individuals may experience skin sensitivity in the underarm area. The most common issue is contact dermatitis, which can present as redness, itching, or mild irritation.
Potential triggers include:
- Alcohol, often used as a solvent, which may disrupt the skin’s natural moisture barrier
- Synthetic fragrances, which can provoke allergic reactions in sensitive or reactive skin
Understanding your skin type is key when choosing a deodorant. For beginners or those with sensitive skin, fragrance-free or alcohol-free formulas may help reduce irritation while still providing effective odor control.
What Is Antiperspirant and How Does It Work?
Unlike deodorant, antiperspirant plays a more active role in managing underarm moisture. According to Dr. Teresa Song, MD, FAAD, antiperspirants are designed to directly reduce sweat production by temporarily limiting sweat release at the skin’s surface.
This effect occurs when the product penetrates sweat ducts and forms a temporary plug. Dr. Hooman Khorasani, MD, FAAD, explains that this mechanism relies on aluminum-based active ingredients, which are widely studied and used in dermatology.
Common ingredients include:
- Aluminum chlorohydrate, which safely reduces sweat flow
- Aluminum zirconium, often used for stronger, longer-lasting protection
Modern antiperspirants come in various user-friendly formats, including sticks, roll-ons, and fast-drying sprays. These innovations allow effective sweat control without a heavy or sticky feel, making antiperspirant a practical choice for individuals with excessive sweating or physically active lifestyles.
Antiperspirant Benefits and Medical Considerations
According to Dr. Teresa Song, MD, FAAD, the primary advantage of antiperspirant lies in its ability to temporarily reduce underarm moisture. By limiting sweat production, the environment that supports bacterial growth becomes less favorable, which helps control body odor more effectively. This makes antiperspirant especially beneficial for individuals with hyperhidrosis or excessive sweating that cannot be managed by deodorant alone.
That said, a transparent medical perspective is important. Some considerations include:
- Visible residue, as aluminum-based ingredients may leave white marks on clothing
- Skin sensitivity, including irritation or allergic reactions, particularly in sensitive skin
Concerns about long-term health effects are often discussed. Dr. Song notes that while aluminum has been studied in relation to breast cancer and Alzheimer’s disease, current scientific evidence remains limited. The American Cancer Society reports that most studies have not found a direct link between antiperspirant use and cancer. Similarly, although elevated aluminum levels have been observed in Alzheimer’s patients, researchers have not confirmed whether this is a cause or a consequence of the disease.[1Klotz* K, Weistenhöfer* W, Neff F, Hartwig A, Thriel C van, Drexler H. The health effects of aluminum exposure. Deutsches Ärzteblatt International. 2017;114(39):653.]
Deodorant vs. Antiperspirant: Key Differences Explained
The fundamental difference between deodorant and antiperspirant lies in how they address sweat. Deodorant focuses solely on controlling body odor by neutralizing bacteria, without reducing sweat production. Antiperspirant, on the other hand, uses aluminum-based compounds to temporarily block sweat glands, helping reduce both moisture and odor.
Dr. Hooman Khorasani, MD, FAAD, and Dr. Teresa Song, MD, FAAD, emphasize that despite their different mechanisms, both products share similar application methods and are available in comparable formats, including sticks, gels, and sprays.
From a medical and regulatory standpoint:
- Antiperspirants are classified as over-the-counter (OTC) drugs because they contain active ingredients that affect physiological function
- Deodorants are considered cosmetic products and often rely on ingredients such as baking soda, magnesium, or tapioca starch to manage odor and absorb moisture naturally
Choosing between the two depends on whether your main goal is odor freshness or comprehensive sweat control.
How to Know Which One Is Best for You
Choosing between deodorant and antiperspirant ultimately depends on your primary concern. If your main goal is to control body odor while allowing your body to sweat naturally, deodorant is usually sufficient. However, if excessive underarm moisture causes discomfort, visible sweat marks, or persistent odor, antiperspirant offers a more effective, medically supported solution.
Dr. Teresa Song, MD, FAAD, and Dr. Hooman Khorasani, MD, FAAD, agree that skin safety should always come first—especially for beginners in personal care. To reduce the risk of irritation or contact dermatitis, consider these practical tips:
- Choose minimalist formulas, preferably fragrance-free, to lower sensitivity risk
- Look for soothing ingredients such as aloe vera to help support the skin barrier
- Opt for hypoallergenic options, particularly when using aluminum-based antiperspirants
If you have a history of allergies, eczema, or ongoing skin concerns, consulting a dermatologist is strongly recommended. An honest assessment of your body’s needs will help you find a product that feels comfortable, effective, and safe for long-term use.
Best Time to Apply Antiperspirant: Why Nighttime Works Better
Many people apply antiperspirant in the morning after showering, but dermatologically, this timing is not ideal. Dr. Teresa Song, MD, FAAD, explains that nighttime application—before bed—is significantly more effective. This is because sweat glands are less active during sleep, allowing the product to work without interference from active perspiration.
From a scientific standpoint, aluminum-based antiperspirants need time to penetrate sweat ducts and form temporary plugs. When applied in the morning, increased physical activity and sweating can wash the product away before it fully activates.
Key benefits of nighttime application include:
- Optimal absorption, as dry and calm skin allows deeper penetration into sweat ducts
- Longer-lasting protection, with effects that can last up to 24 hours, even after a morning shower
Dr. Hooman Khorasani, MD, FAAD, particularly recommends this method for individuals with hyperhidrosis to achieve better sweat control without frequent reapplication.
Deodorant for Sensitive Skin: Preventing Clogged Pores
Clogged pores and underarm inflammation are often caused by product buildup combined with dead skin cells. According to Dr. Hooman Khorasani, MD, FAAD, unresolved buildup may lead to chronic irritation or underarm breakouts. For sensitive skin, choosing non-comedogenic formulas is essential to maintain skin health.
Dr. Teresa Song, MD, FAAD, advises selecting products with barrier-supporting and soothing ingredients. To help prevent pore blockage and irritation, consider the following tips:
- Choose water-based formulas, such as gels or sprays, which are lighter than wax-heavy sticks
- Practice gentle exfoliation, using salicylic acid (BHA) cleansers occasionally to remove residue and excess oil
- Avoid alcohol, as it can cause excessive dryness and trigger compensatory oil production
Healthy underarm care is not just about odor control—it’s about keeping the skin calm, breathable, and free from inflammation.
Final Thoughts
Choosing between deodorant and antiperspirant is a personal decision based on your body’s physiological needs. If odor control is your main concern, deodorants with antimicrobial ingredients are often sufficient. However, if excessive sweating disrupts daily comfort, aluminum-based antiperspirants provide more effective moisture control.
Dr. Teresa Song and Dr. Hooman Khorasani emphasize the importance of protecting the skin barrier. Whether you prefer natural or conventional formulas, fragrance-free options can help reduce irritation risk. Optimizing application timing—especially at night—and incorporating gentle exfoliation into your routine can further support healthy, clear pores.
An honest understanding of your skin, combined with informed product choices and professional guidance when needed, will help ensure long-term comfort, skin health, and everyday confidence.





 Acne
Acne Anti-Aging
Anti-Aging Business
Business Digital Marketing
Digital Marketing Economics
Economics Exfoliation
Exfoliation Hair Removal
Hair Removal Movies
Movies Personal Finance
Personal Finance Websites
Websites